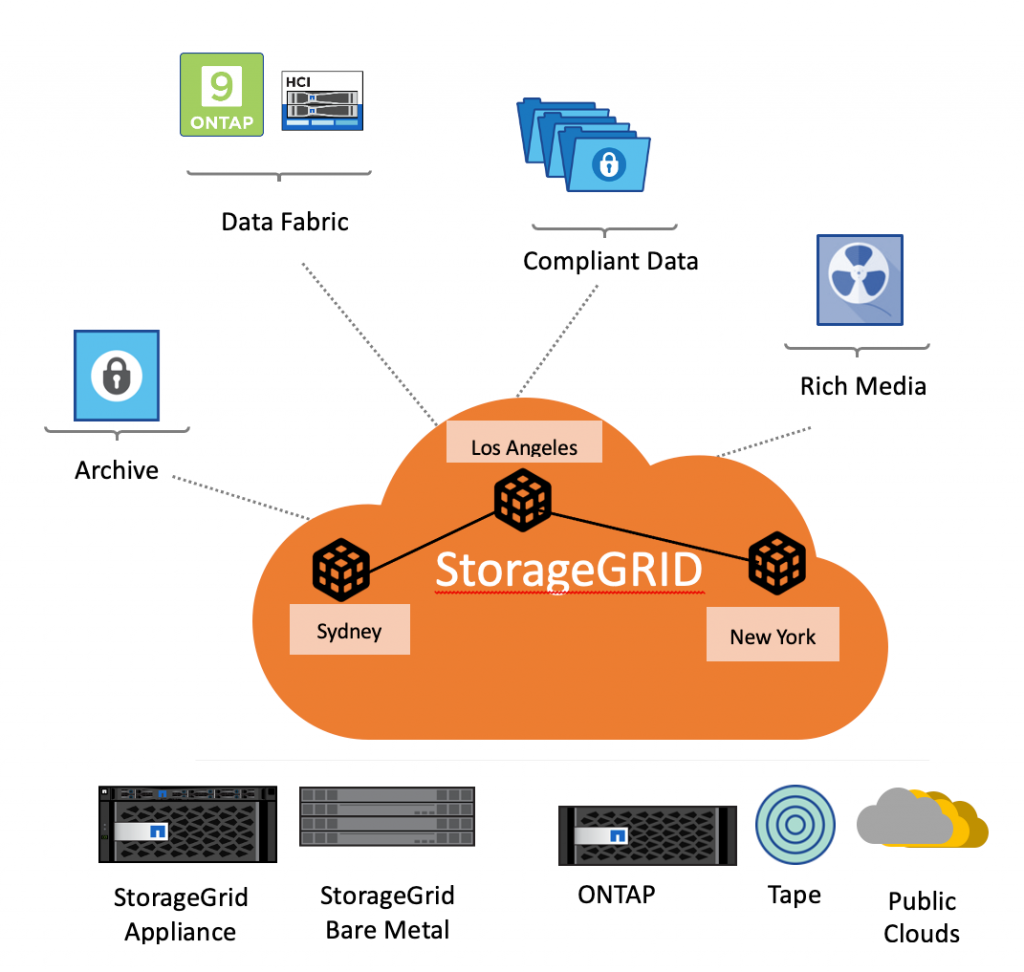
A topic that keeps coming up in conversations is NetApp StorageGrid and how it fits in the data fabric.
During the next few blog posts, I will be going over what is NetApp StorageGrid, how to Deploy StorageGrid, how to connect a NetApp FabricPool to a StorageGrid, how to upgrade the firmware on StorageGrid, how to expand the StorageGrid, and lastly how to Extend Tiering Object workflows to the Cloud.
What is Object Storage
Object storage, also known as object-based storage, is a strategy that manages and manipulates data storage as distinct units, called objects.
These objects are kept in a single location and are not integrated with files inside other folders.
Instead, object storage combines the pieces of data that make up a file, adds all its relevant metadata to that file, and attaches a custom identifier.
Object storage adds comprehensive metadata to the file, eliminating the tiered file structure used in file storage, and places everything into a flat address space, called a storage pool.
Object Storage vs. File Storage vs. Block Storage
Object Storage
Object storage takes each piece of data and designates it as an object. Data is kept in separate storehouses versus files in folders and is bundled with associated metadata and a unique identifier to form a storage pool.
File Storage
File storage stores data as a single piece of information in a folder to help organize it among other data. This is also called hierarchical storage, imitating the way that paper files are stored. When you need access to data, your computer system needs to know the path to find it.
Block Storage
Block storage takes a file apart into singular blocks of data and then stores these blocks as separate pieces of data. Each piece of data has a different address, so they don’t need to be stored in a file structure.
Benefits of Object Storage
Now that we’ve described what object storage is, what are its benefits?
Now that we’ve described what object storage is, what are its benefits?
- Greater data analytics. Object storage is driven by metadata, and with this level of classification for every piece of data, the opportunity for analysis is far greater.
- Infinite scalability. Keep adding data, forever. There’s no limit.
- Faster data retrieval. Due to the categorization structure of object storage, and the lack of folder hierarchy, you can retrieve your data much faster.
- Reduction in cost. Due to the scale-out nature of object storage, it’s less costly to store all your data.
- Optimization of resources. Because object storage does not have a filing hierarchy, and the metadata is completely customizable, there are far fewer limitations than with file or block storage.
Cloud and Object Storage
Cloud object storage is a format for storing unstructured data in the cloud. Object storage is considered a good fit for the cloud because it is elastic, flexible and it can more easily scale into multiple petabytes to support unlimited data growth.
NetApp and Object Storage
Store and manage unstructured data at scale by using NetApp StorageGRID for secure, durable object storage for the private and public cloud. Place content in the right location, at the right time, and on the right storage tier, optimizing workflows and reducing overall costs for globally distributed rich media.
What is StorageGrid
StorageGRID is a software-defined, object-based storage platform that provides intelligent policy-driven data management.
StorageGRID stores and manages unstructured data at scale to provide secure, durable object storage.
Benefit of StorageGrid
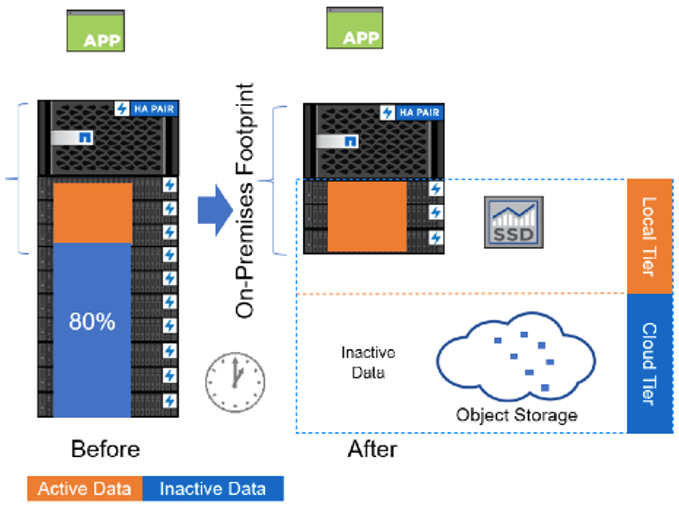
FabricPool
FabricPool is a NetApp Data Fabric technology that enables automated tiering of data to low-cost object storage located in the public and private cloud. SSD storage is fast but expensive, so ideally you want to limit SSD use to only workloads that actively require it. FabricPool offers a policy-driven means for selecting and moving (tiering) certain categories of data from your SSD storage (the internal tier) to more cost-effective object storage (the cloud tier).
To manage objects ingested into the system, the StorageGrid Webscale system employs metadata-based information lifecycle management (ILM) rules.
These ILM rules determine what happens to an object’s data after it is ingested—where it is stored, how it is protected from loss, and how long it is stored.
The StorageGrid Webscale system operates over a wide area network (WAN) links, providing the system with off-site loss protection. Copies are made and distributed to ensure that objects are continuously available. In systems with multiple sites, this distribution of copies means that if a site is lost, data is not lost, and clients can seamlessly retrieve it from other sites.